There are generally 3 types of Trading Styles: Intraday / Swing / Long-Term
Intraday
Intraday futures trading refers to the practice of buying and selling futures contracts within a single trading day, as opposed to holding positions overnight or for a longer period of time. This type of trading can be a fast-paced and high-risk activity, as traders must be able to quickly analyze market conditions and make informed decisions within a short time frame.
Intraday futures traders typically rely on a variety of tools and techniques to help them identify trading opportunities and make informed decisions. These may include technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both. Technical analysis involves studying charts and other market data to identify trends and patterns that may indicate future price movements, while fundamental analysis involves analyzing economic, political, and other factors that may impact the value of a particular asset or market.
Traders who engage in intraday futures trading may use a variety of strategies to try to capitalize on short-term price movements in the market. These may include trend-following strategies, breakout strategies, or scalp trading, among others. It is important for traders to carefully consider the risks and potential rewards of each strategy, as well as the level of experience and expertise required to execute them effectively.
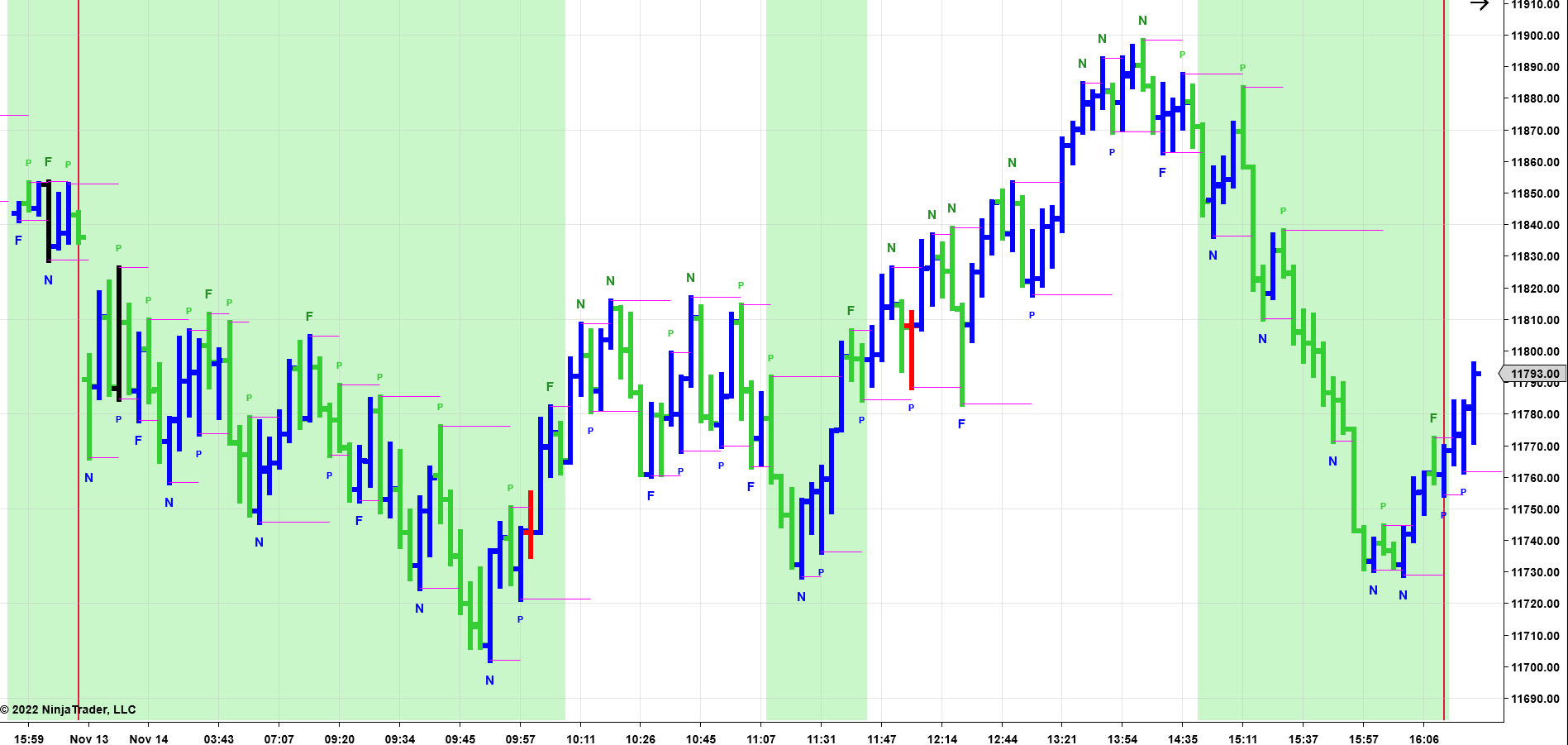
Here is an example of an Intraday Trading Chart of the Nasdaq-100 using a Constant Volume Bar Chart with the PRICEPhysics GUI applied
Swing
Swing futures trading involves holding positions in the futures market for a period of time that is longer than a single trading day, but shorter than a long-term investment. This type of trading can be a suitable strategy for investors who are looking to capitalize on intermediate-term price movements in the market, and who are willing to hold positions for a longer period of time than is typical in intraday trading.
Swing traders typically use technical analysis and chart patterns to identify potential trading opportunities in the futures market. They may also consider fundamental factors such as economic and political news, as well as market sentiment, in order to make informed trading decisions.
There are a variety of strategies that swing traders may use to try to profit from intermediate-term price movements in the futures market. These may include trend-following strategies, range-bound strategies, or breakout strategies, among others. It is important for swing traders to carefully consider the risks and potential rewards of each strategy, and to choose a strategy that is appropriate for their level of experience and risk tolerance.
One of the main advantages of swing futures trading is that it allows traders to potentially capitalize on intermediate-term price movements in the market, without the need to constantly monitor their positions or make frequent trades. This can be particularly appealing for traders who have other commitments or who are looking to trade the futures market on a part-time basis.
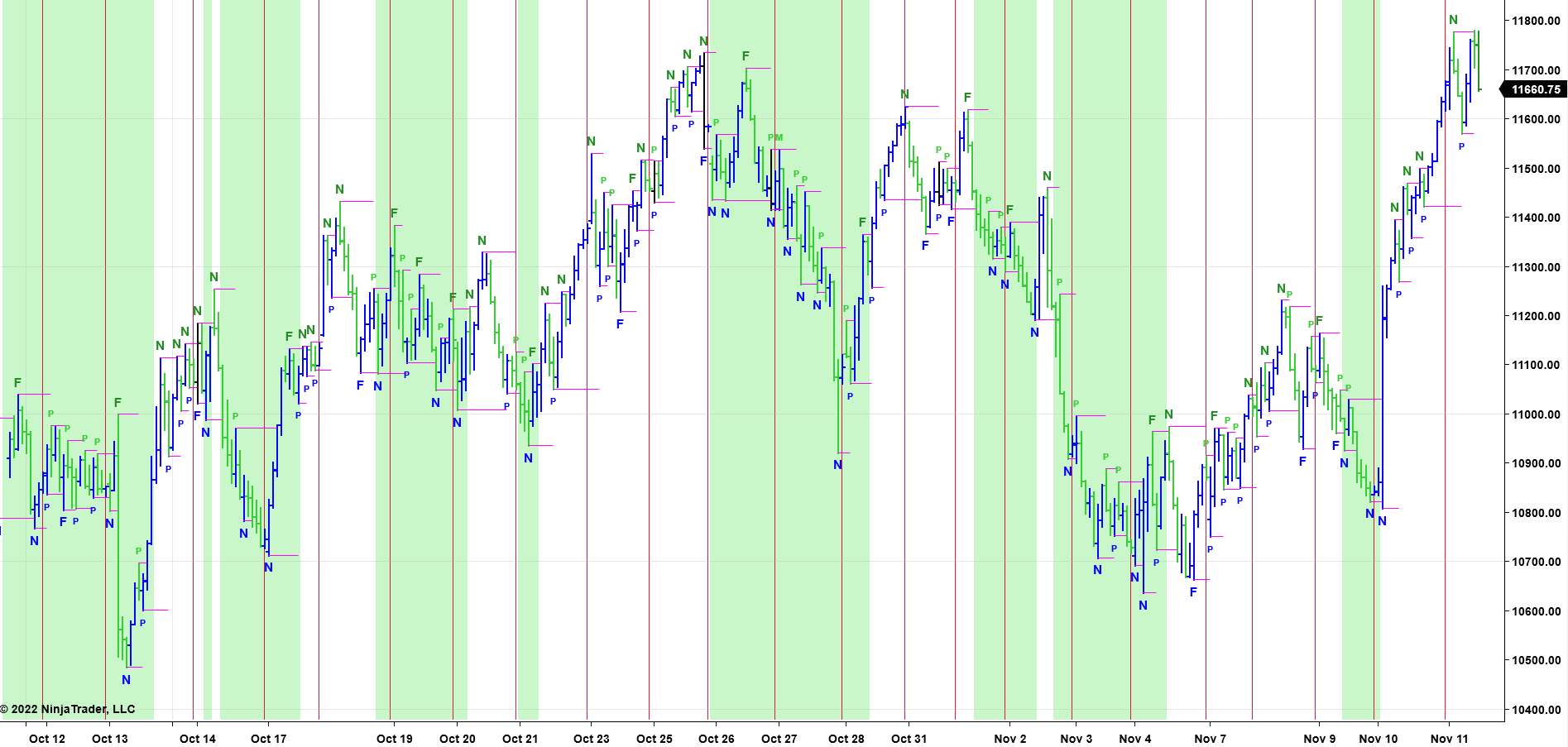
Here is an example of an Swing Trading Chart of the Nasdaq-100 using a Constant Volume Bar Chart with the PRICEPhysics GUI applied
Long-Term
A long-term futures trading strategy involves holding positions in the futures market for an extended period of time, typically longer than a few months. This type of strategy is typically pursued by investors who are looking to capitalize on long-term price trends in the market, rather than short-term fluctuations.
One common long-term futures trading strategy is to buy and hold a position in a futures contract that is expected to appreciate in value over time. This can involve holding a position in a contract that is tied to an underlying asset such as a commodity or currency that is expected to increase in value over time due to factors such as rising demand, improving economic conditions, or other favorable trends.
Another long-term futures trading strategy is to use a diversified portfolio of futures contracts to take advantage of price movements in a variety of different markets. This can involve holding a mix of contracts tied to different underlying assets, such as commodities, currencies, and indices, in order to spread risk and potentially increase the chances of realizing profits over the long term.
It is important to note that long-term futures trading carries its own set of risks and challenges, and it is not suitable for all investors. It is essential for traders to carefully consider their risk tolerance and financial objectives before engaging in this type of trading, and to seek the guidance of a financial professional if necessary. Despite the risks, however, long-term futures trading can offer the potential for significant profits over the long term, and it can be a rewarding strategy for those who are able to successfully navigate the complex and constantly-changing futures market.
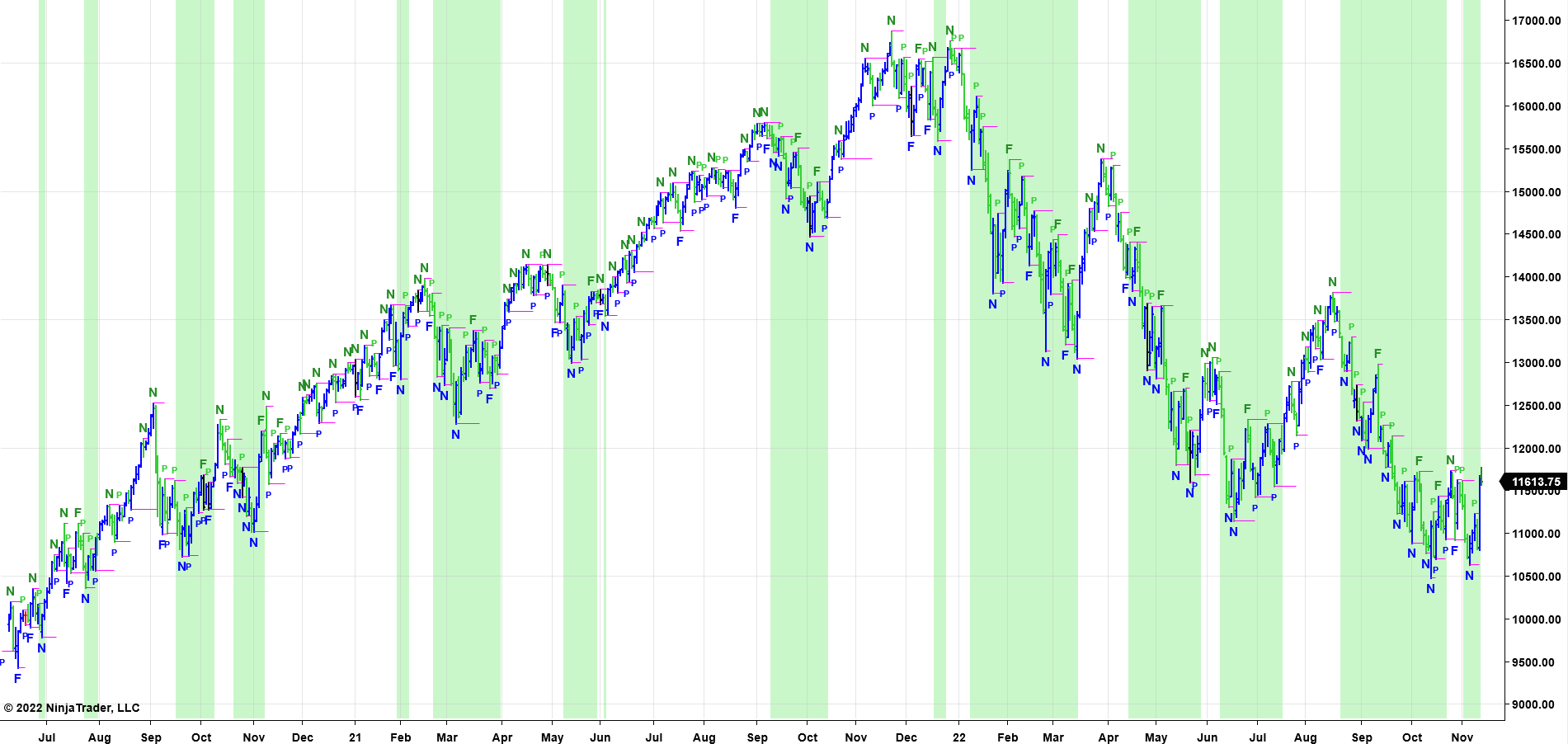
Here is an example of an Long Term Trading Chart of the Nasdaq-100 using a Constant Volume Bar Chart with the PRICEPhysics GUI applied